Individuals with diabetes have to test their blood sugar levels frequently. There are a variety of different methods in common use today.
Fingerprick

The most widely-used method of testing blood sugar uses a test strip, a meter, and a drop of blood drawn from a finger. A tiny lancet is used to prick the finger. The resulting drop of blood is placed on a test strip. The test strip is saturated with an enzyme (either glucose oxidase or hexokinase). The enzyme reacts with the glucose in the blood. The test strip is then fed into a glucose meter, which reads the test strip and immediately returns a measurement of blood glucose level in terms of of mg/dl. Depending on the meter design, it is either reading a color change caused by the enzyme reacting with glucose, or measuring an electric current produced by the enzyme’s reaction with glucose.
Alternative sites
Some glucose meters allow for testing blood from sites other than the fingertip. Many diabetics get very sore fingertips over time and appreciate the ability to test different sites, such as the upper arm or calf. However, fingertip testing reflects changes in blood glucose levels more rapidly than other sites, and therefore alternative sites should not be used during times when blood sugar may be changing rapidly, such as after a meal or after exercising.
Continuous glucose monitoring
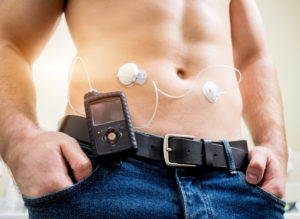
A continuous glucose monitor measures blood sugar levels around the clock. A tiny sensor is implanted under the skin of the abdomen or upper buttock. An adhesive patch placed on the skin holds the sensor in place. The sensor is connected to a tiny transmitter that sends information wirelessly to a small monitoring device that can be clipped to the waistband or placed in a pocket. The information collected by the device can be downloaded to a computer or smartphone. It can also be linked to an insulin pump. The sensors have to be replaced every few days, but the insertion procedure is simple and relatively painless. Continuous glucose monitors do need to be regularly calibrated to the results of fingerstick glucose tests.
Freestyle libre
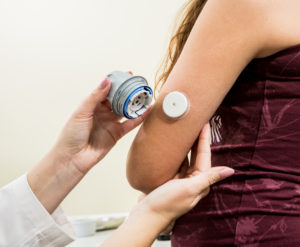
Advertised as a painless monitoring system, it is currently only available in Europe. A tiny filament is inserted into the skin of the arm and is held in place with an adhesive pad. A small hand-held scanner is passed over the filament to measure glucose levels. The scanner can detect the filament through clothing, allowing for discreet testing at any time or place. The filament only has to be replaced every two weeks, and fingerstick testing for calibration of the device is not necessary.
I started to drink soft drinks right after every meal. and then I started to feel something unusual with my body. i felt like I’m a bit lazy, like i don’t want to get off of bed. i decided to check my sugar level and it was 320mg/dl already!!
I’m avoiding now drinking soda. for a month i will try to have my sugar level tested again.
yes i agree josie the sugary sodas hey even those diet one send the body into turmoil. they are not helping anybody. eliminating just one thing can make all the difference
After eating.low blood sugar 97 that ok?
I have diabetes type 2 and I keep checking my sugar level like 4 times daily
and I don’t know why is reading like this : 101 mg before breakfast
107 mg two hours after lunch
133 mg in the afternoon (around 3:10 pm)
I don’t know if it’s me or the glucometer , can somebody tell me what’s wrong ?
I’m a type 2 diabetic and I have a lot of canned fruit and vegetables from the food bank and was wondering which to avoid